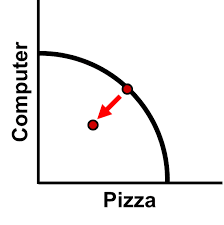
UNIT 1: business cycle & price ceiling/floor
- Equilibrium- is the point at which the supply curve & demand curve intersect:

- excess demand- when quantity demand is greater than quality supplied. results in shortage.
- shortage- consumers cannot get enough of the quantities they desire.
- price ceiling- creates a shortage. occurs when the government puts a legal limit on how high the price of a product can be.
- excess supply- supply is greater than demand
- price floor- lowest legal price something can be sold for. prevents prices from becoming too low.
- business cycle:
- 1 cycle is from trough to trough
- average cycle is 5-7 years
- recessions last about 14 months
- peaks and troughs are meaningless because we usually don't notice until it's over
- trough is the end of a recession
- if the recession takes more than 10 of the CPP, than it is a depression