Aggregate demand curve
- AD is the demand by consumers, businesses, government, and foreign countries
- Changes in price level cause a move along the curve. Not a shift of the curve
- The relationship between the price level and real GDP is inverse
- Three reasons why AD is downward sloping:
- wealth effect- higher price is reduced purchasing power of money. This decreases the quantity of expenditures. Lower price levels increase purchasing power and increase expenditures
- Interest rate effect – as price level increases, lenders need to charge higher interest rates to get a real return on their loans. Higher interest rates discourage consumer spending and business investment
- Foreign trade effect – when US price levels rise foreign buyers purchase if you were US goods and Americans buy more foreign goods. Exports fall and imports rise causing real GDP demand to fall. (Xn decreases)
- Shifts in aggregate demand
- Change in C, I, G, Xn
- Multiplier effect that produces a greater change in the original change in the 4 components
- Increase in AD causes shift to the right
- Decrease in AD causes shift to the left
Determinants of aggregate demand:
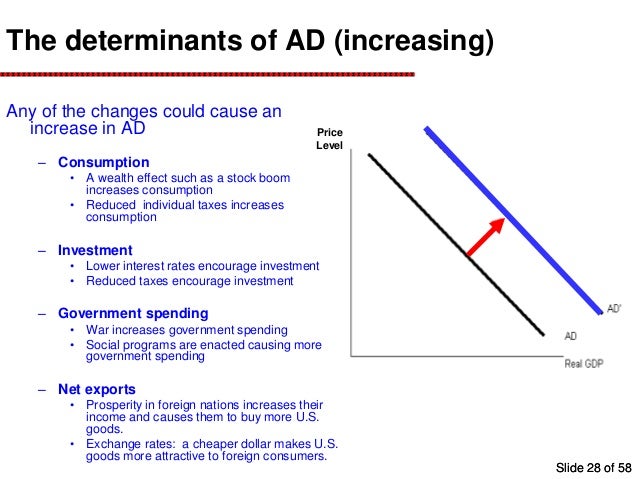


- C-(consumption)
- Change in consumer spending. Consumer wealth(boom in the stock market). Consumer expectation(people fear a recession). Household indebtedness (more consumer debt). Taxes(decrease in income taxes)
- Change in investment spending:
- Real interest rates (price of borrowing money)
- Future business expectations (high expectations)
- Productivity and technology (new robots…)
- Business taxes (higher corporate taxes means..)
- Change in government spending
- War
- Nationalized healthcare
- Fear causes an increase in defense spending
- More spending- AD goes to the right
- Less spending- AD goes to the left
- Change in net exports
- Exchange rates (if the U.S. dollar depreciates relative to the euro)
- National income compared to abroad (if major importer has a recession)
- “If US gets a cold, Canada gets pneumonia”
No comments:
Post a Comment